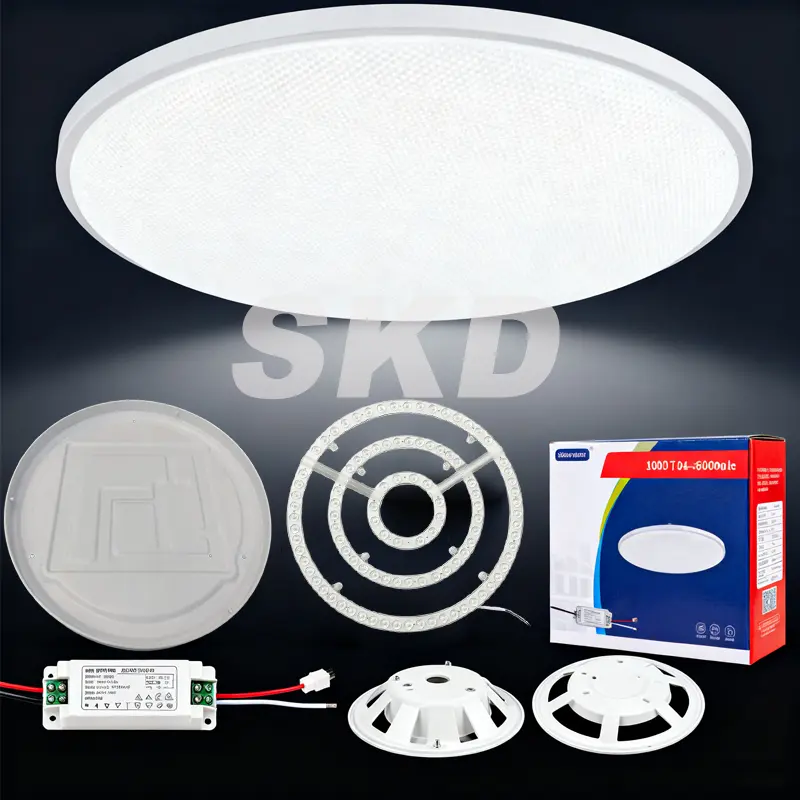
Industry Tips--Knowledge of LED Optical Design
What are Primary Optical Design and Secondary Optical Design of LEDs? Do all LEDs include both? Below is a concise overview of core LED optical design knowledge.
I. Primary Optical Design
A mandatory process for all LEDs: Conducted during LED chip packaging into optoelectronic components, focusing on optimizing five core optical parameters: light emission angle, light intensity, luminous flux, light intensity distribution, and color temperature range/distribution.
Key design objects: Chip, bracket, mold
*Chip: Adjust arrangement and luminous surface for initial light distribution;
*Bracket: Optimize reflective cup angle/coating to boost light extraction;
*Mold: Control light propagation via encapsulant refractive index and shape.
Key Conclusion: All LEDs require primary optical design—without it, chips cannot achieve directional emission or stable performance.

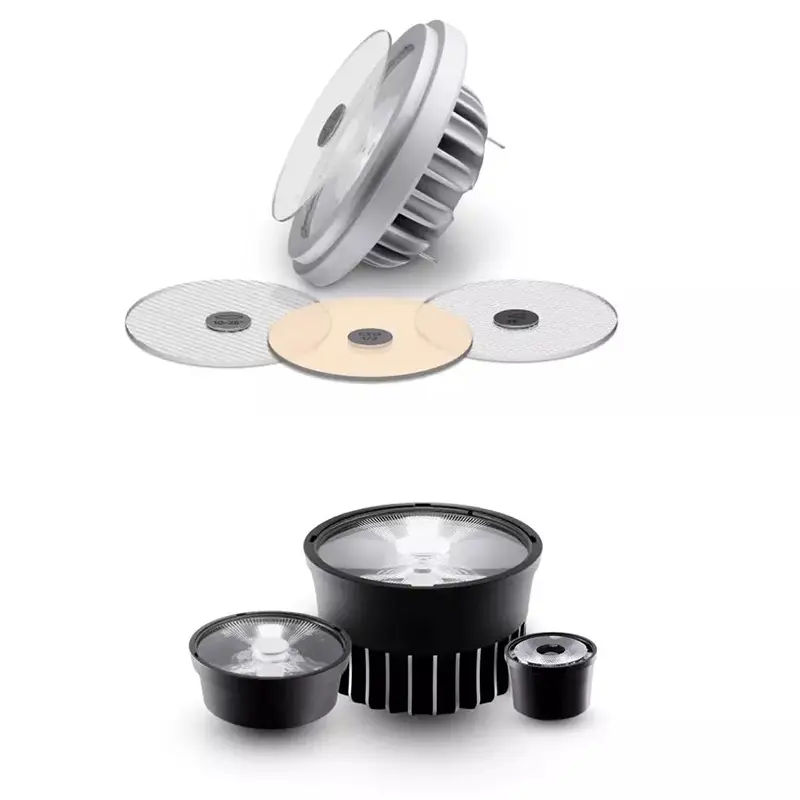
II. Secondary Optical Design
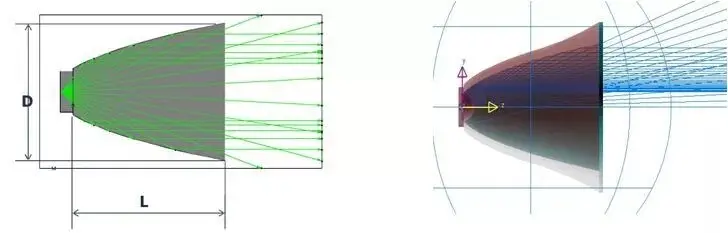
Targeted at high-power Led Lighting products: Modifies light from the primary lens (≈120° emission angle) via additional optical elements to meet specific application needs.
Core purposes:
1.Precise light control (narrow/flood beams, special shapes like bat-wing distribution);
2.15-30% higher light utilization efficiency;
3.Reduced glare, improved spot uniformity.
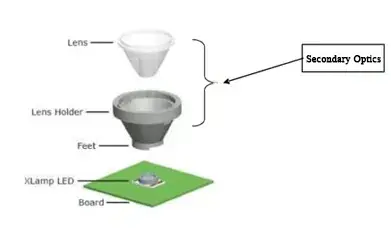
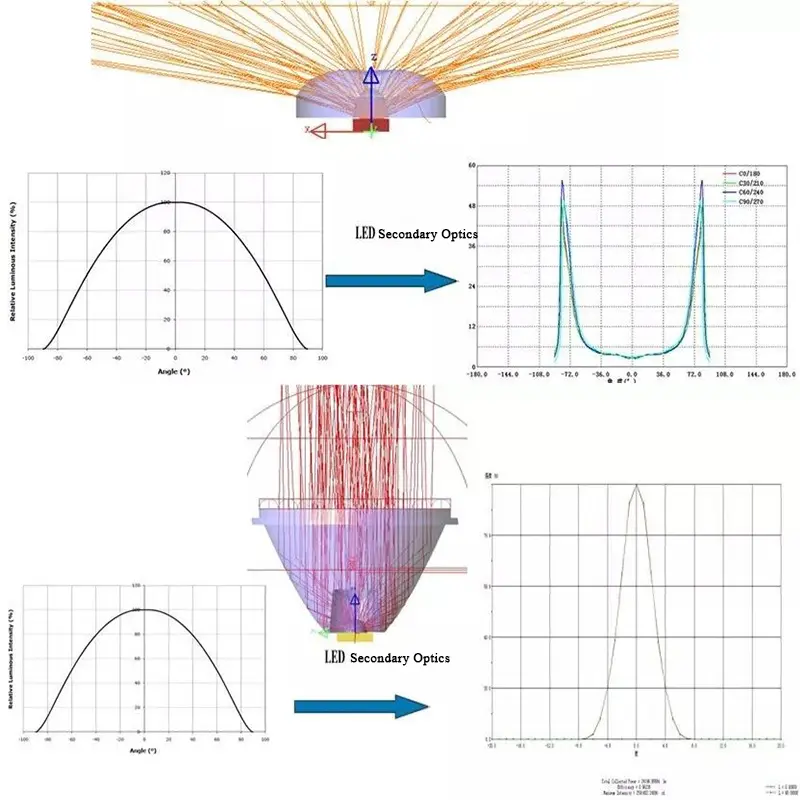
III. Secondary Optical Design Principles
Illuminance at any point in the target area is formed by light energy redistribution and superposition through a system:
LED Source (after primary design) + Secondary Optical System + Illuminated Plane
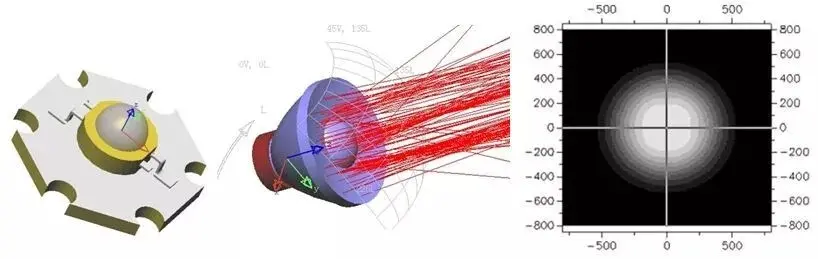
1-Define scene requirements (illuminance, spot shape, glare level);
2-Eliminate unfeasible demands;
3-Layout optical elements (lens/reflective cup) and positions;
4-Optimize via simulation software (Zemax, TracePro);
5-Generate processable product drawings.
V. Application Scenarios & Key Testing
*Typical Scenarios:
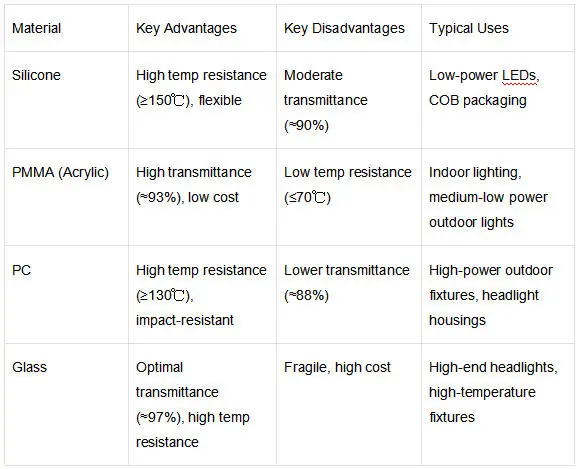
Street lighting (aspheric lens + reflective cup for bat-wing distribution); indoor downlights/spotlights (convex lens + light shield for narrow beams); floodlighting (large-diameter PMMA/PC lenses); automotive headlights (glass lens + metal reflective cup for high temperature resistance).
*Core Testing:
Simulation (ray tracing, thermo-optical coupling); physical tests (light distribution curve, illuminance, UGR glare rating, high-low temperature reliability).
1-Reflective Cup Type: Simple, low-cost, suitable for light concentration (flashlights); limited precision.
2-Lens Type: Mainstream option, high precision, uniform spots (Indoor Lighting, headlights).
3-Combination Type: Merges concentration (cup) and uniformity (lens) for high-power precision lighting.
Key Conclusion: Lenses are more effective than reflectors for complex light shape adjustments.